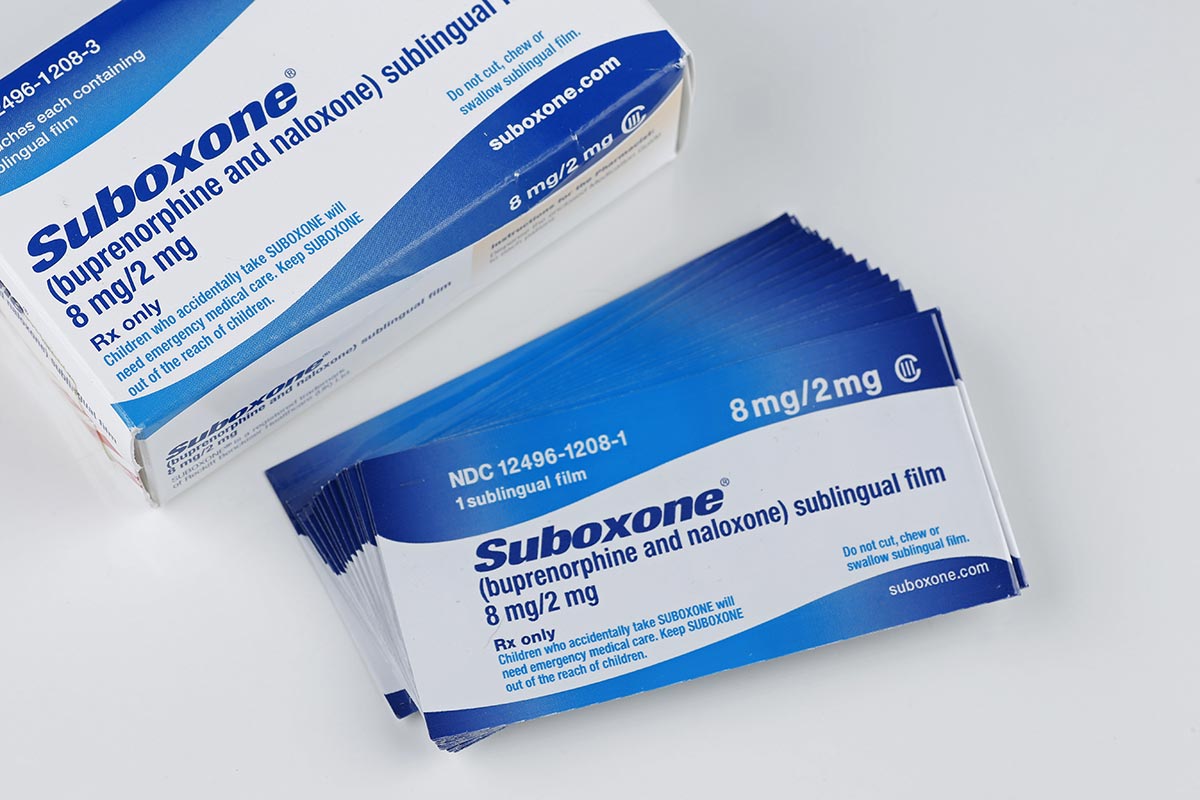
Suboxone is an FDA-approved prescription drug most commonly used to help people maintain abstinence from opioid drugs. As a result, suboxone is one of the most prescribed medications for Medication Assisted Treatment (MAT) programs. It’s also listed as a life-saving drug by the World Health Administration as an essential drug. At the same time, there’s a lot of controversy around Suboxone – both for use with opioids and also for extra strong opioids such as fentanyl.Here, many people are concerned that they’re replacing one drug with another. Others are concerned that Suboxone also has a withdrawal period. And, in some cases, individuals are concerned about the potential of precipitated withdrawal, which means that you suddenly go into withdrawal from a very strong drug, which can result in hospitalization.
At the same time, Suboxone is considered one of the most important drugs for helping people maintain recovery – so you don’t run the risk of overdose when you go back to fentanyl. What are the factors that impact this? And, how effective is it?
What is Suboxone?
Suboxone is an FDA-approved combination drug composed of Buprenorphine and Naloxone. It’s typically orally administrated and is primarily used in maintenance programs to help individuals stay clean during recovery from opioid use disorder. The drug has been shown to greatly improve outcomes for individuals by preventing relapse, reducing cravings, and reducing the length and severity of the detox phase. It’s also comprised of two of the most important drugs in opioid use disorder treatment:
- Buprenorphine – Buprenorphine is an opioid drug with a light side effect profile and a lower addiction profile than those used recreationally. In light doses, buprenorphine causes no euphoria or sedation, meaning that it doesn’t have a driver for individuals to abuse it recreationally. However, it does bind with the same opioid receptors in the body and brain as fentanyl, meaning that while you’re taking it, you don’t experience physical cravings and you don’t go into withdrawal. This drug is sold on its own as Subutex. Here, it’s an important and lief-saving drug. However, it still carries the potential of abuse as buprenorphine can cause euphoria in high doses and when injected.
- Naloxone – Suboxone also contains Naloxone, which is known as a the opioid overdose withdrawal reversal drug. Naloxone is an opioid antagonist which causes opioids to stop binding with receptors in the brain. This can pull individuals out of an overdose. It can also cause sudden onset withdrawal which means that someone taking Naloxone suddenly will almost certainly require hospital care and treatment. However, it’s poorly digested orally. This means that while you are taking the Suboxone orally or according to prescription, it won’t have an effect. However, if you take more than the prescribed dose or attempt to inject it, the Naloxone will take effect – and you will go into withdrawal.
In short, Suboxone is buprenorphine, an opioid drug with an anti-abuse mechanism built in. That makes it safer for people to take home and use on their own, even during early stages of addiction.
When taking it, you should mostly feel normal, but without cravings or withdrawal symptoms associated with quitting opioid drugs like fentanyl.
Get Your Questions Answered
Our expert & caring staff on site are available 24/7. Call us today.
Is Suboxone Effective?
Suboxone is one of the most-recommended drugs for medication assisted treatment. That recommendation comes from the fact that it works, it has a very low risk of abuse, and the safety mechanism of Naloxone means that patients can more easily use it unsupervised at home. That allows more freedom to individuals to live their lives rather than going to a doctor’s office or clinic every day for a dose of buprenorphine.Suboxone is also fully FDA approved. It’s consistently pointed to as greatly improving outcomes in opioid use disorder treatment. However, it is not a treatment on its own. Suboxone does not help you overcome behavioral addiction. Instead, it reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms, allowing you to go about living your normal life while getting treatment for substance use disorder.
Without dealing with cravings, you’re more likely to be able to get through treatment without risking relapse and potential overdose on fentanyl. This means it greatly reduces risks of accidental death while also reducing risk of relapse to begin with. At the same time, you still need behavioral therapy to recover from a behavioral substance use disorder. For this reason, any substance use disorder treatment program offering medication assistance with Suboxone will pair it with therapy and counseling.
Overall, Suboxone is a very safe and effective drug that can function as a crutch while you learn the skills to stay clean. It reduces the impact of quitting right away, reduces cravings, and lowers the threshold to staying clean. As a result, people who use it are significantly more likely to stay in recovery than those who are not in a MAT program.
What’s are the Concerns of Using Suboxone with Fentanyl?
Fentanyl is widely known as one of the strongest opioid drugs on the market. It’s also increasingly finding its way into dozens of drugs, including faux prescription pills, drugs sold as heroin, and even directly sold as fentanyl. At 10,000 times the strength of morphine, fentanyl is extremely strong and has a very high risk of overdose and accidental drug death. In fact, more than 74% of opioid drug deaths are linked to fentanyl. When you use Naloxone to treat fentanyl overdose, it causes significant and immediate withdrawal symptoms which can require medical attention. This is known as precipitated withdrawal. Persons taking suboxone run a risk of precipitated withdrawal as well. However, according to a study published in 2023, about 1% of fentanyl users taking suboxone will go through precipitated withdrawal. This means that it is important to start using suboxone in a clinic if you’re a fentanyl user. However, risks are extremely low.
In other cases, people are concerned about using one opioid to recover from another. However, buprenorphine has an extremely low addiction profile. This means it’s very unlikely that you become addicted to the drug. You will become dependent on the drug, which means you’ll have to taper off it in order to quit. However, it also means you can safely quit opioids, with low risks of strong withdrawal symptoms, and low risk of relapse. As a result, Suboxone is associated with improved recovery rates, reduced risk of death, and decreased cost of treatment.
Seeking Out Medication Assisted Treatment
If you or a loved one is struggling with substance abuse, it’s important to look into getting help. If that substance is fentanyl, withdrawal and recovery are difficult and can be dangerous. Medication assisted programs with Suboxone can greatly reduce those risks. However, it’s important to discuss your options with your doctor and your rehab facility. Both should help you to look at your options, associated risks, and how those risks come into play for your recovery, your long-term health, and your short-term treatment. Chances are very high that you’ll be recommended into a tapering program to reduce fentanyl usage or directly into a detox clinic where you can start suboxone under medical supervision and then directly into a behavioral mental health treatment program.
Eventually, the right treatment for you depends on your mental health, your addiction, and what you want for yourself. Suboxone can be life-saving, it can reduce risks, and it can help you to stay in recovery. Either way, good luck getting treatment.






